10th class pratice
Create a class named Pizza that stores details about a pizza. It should contain the following:
Instance Variables:
String pizzaSize — to store the size of the pizza (small, medium, or large)
int cheese — the number of cheese toppings
int pepperoni — the number of pepperoni toppings
int mushroom — the number of mushroom toppings
Member Methods:
Constructor — to initialise all the instance variables
CalculateCost() — A public method that returns a double value, that is, the cost of the pizza.
Pizza cost is calculated as follows:
- Small: Rs.500 + Rs.25 per topping
- Medium: Rs.650 + Rs.25 per topping
- Large: Rs.800 + Rs.25 per topping
PizzaDescription() — A public method that returns a String containing the pizza size, quantity of each topping, and the pizza cost as calculated by CalculateCost().
CODE:
public class Pizza { String pizzaSize; int cheese; int pepperoni; int mushroom; public Pizza(String size, int tc, int tp, int tm) { pizzaSize = size; cheese = tc; pepperoni = tp; mushroom = tm; } public double CalculateCost() { double totalCost = 0; double topCost = 25 * (cheese + pepperoni + mushroom); if (pizzaSize == "small") totalCost = 500 + topCost; else if(pizzaSize == "medium") totalCost = 650 + topCost; else totalCost = 800 + topCost; return totalCost; } public String PizzaDescription() { double cost = CalculateCost(); String desc = "Size: " + pizzaSize + " Cheese: " + cheese + " Pepperoni: " + pepperoni + " Mushroom: " + mushroom + " Cost: Rs. " + cost; return desc; } public static void main(String args[]) { Pizza p = new Pizza("medium", 15, 5, 10); String desc = p.PizzaDescription(); System.out.println(desc); } }
Write a program in Java to display the following patterns.
1 * * * * 2 2 * * * 3 3 3 * * 4 4 4 4 * 5 5 5 5 5public class KboatPattern{ public static void main(String args[]) { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { System.out.print(i); } for (int k = 1; k <= 5 - i; k++) { System.out.print('*'); } System.out.println(); } } }Write a program in Java to display the following patterns.
I I C I C S I C S Epublic class KboatPattern { public static void main(String args[]) { String str = "ICSE"; int len = str.length(); for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) { for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) { System.out.print(str.charAt(j) + " "); } System.out.println(); } } }Write a program to print the series given below.
8 88 888 8888 88888 888888
public class Kboat8Series { public static void main(String args[]) { for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { System.out.print('8'); } System.out.print(' '); } } }Question 6
Write a program to generate a triangle or an inverted triangle till n terms based upon the user's choice of triangle to be displayed.
Example 1
Input:
Type 1 for a triangle and type 2 for an inverted triangle
1
Enter the number of terms
5
Output:1 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5Example 2
Input:
Type 1 for a triangle and type 2 for an inverted triangle
2
Enter the number of terms
6
Output:6 6 6 6 6 6 5 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 2 2 1import java.util.Scanner; public class KboatPattern { public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Type 1 for a triangle"); System.out.println("Type 2 for an inverted triangle"); System.out.print("Enter your choice: "); int ch = in.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the number of terms: "); int n = in.nextInt(); switch (ch) { case 1: for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { System.out.print(i + " "); } System.out.println(); } break; case 2: for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { System.out.print(i + " "); } System.out.println(); } break; default: System.out.println("Incorrect Choice"); } } }Write a program to compute and display factorials of numbers between p and q where p > 0, q > 0, and p > q.
import java.util.Scanner; public class KboatFactRange { public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter p: "); int p = in.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter q: "); int q = in.nextInt(); if (p > q && p > 0 && q > 0) { for (int i = q; i <= p; i++) { long fact = 1; for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) fact *= j; System.out.println("Factorial of " + i + " = " + fact); } } else { System.out.println("Invalid Input"); } } }Write a program to determine if an entered number is a Happy Number. A happy number is defined by the following process:
Starting with any positive integer, replace the number by the sum of the squares of its digits, and repeat the process until the number is equal to 1.
For example, 19 is a happy number, as per the following calculation:
12 + 92 = 82,
82 + 22 = 68,
62 + 82 = 100,
12 + 02 + 02 = 1import java.util.Scanner; public class KboatHappyNumber { public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter number to check: "); long num = in.nextLong(); long sum = 0; long n = num; do { sum = 0; while (n != 0) { int d = (int)(n % 10); sum += d * d; n /= 10; } n = sum; } while (sum > 6); if (sum == 1) { System.out.println(num + " is a Happy Number"); } else { System.out.println(num + " is not a Happy Number"); } } }Write a program to input a sentence and print each word of the string along with its length in tabular form.
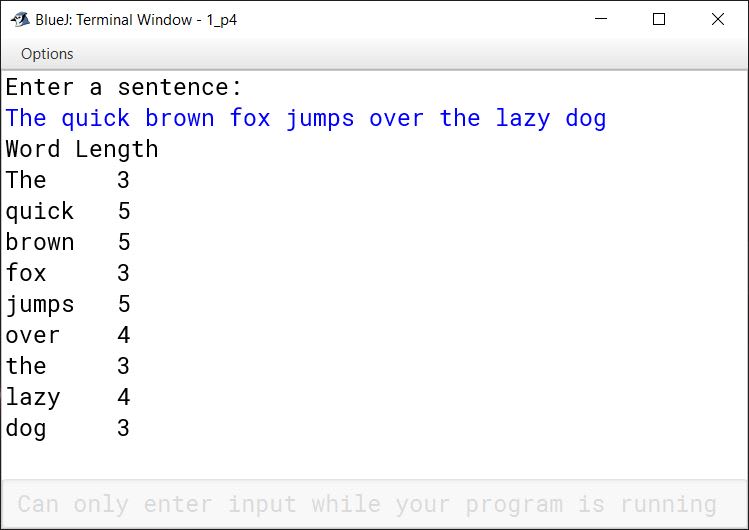
import java.util.Scanner; public class KboatWordsLengthTable { public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter a sentence:"); String str = in.nextLine(); str += " "; int len = str.length(); String word = ""; int wLen = 0; System.out.println("Word Length"); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { char ch = str.charAt(i); if (ch != ' ') { word = word + ch; wLen++; } else { System.out.println(word + "\t" + wLen); word = ""; wLen = 0; } } } }Output
Write a program to input a sentence and arrange each word of the string in alphabetical order.


Comments
Post a Comment